Lapce v0.2.8 - Privilege escalation via Race Condition
7.3
High
Discovered by

Offensive Team, Fluid Attacks
Summary
Full name
Lapce v0.2.8 - Privilege escalation via Race Condition
Code name
State
Public
Release date
Jun 1, 2023
Affected product
Lapce
Affected version(s)
Version 0.2.8
Vulnerability name
Race Condition
Vulnerability type
Remotely exploitable
No
CVSS v3.1 vector string
CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:L/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H
CVSS v3.1 base score
7.3
Exploit available
Yes
CVE ID(s)
Description
Lapce v0.2.8 contains a logical vulnerability in its code that could potentially allow an attacker to escalate their privileges on the server. This vulnerability arises when downloading a file remotely to a location where an attacker can manipulate the downloaded file. The issue is attributed to a Race Condition vulnerability in the code.
Vulnerability
An identified vulnerability in Lapce v0.2.8 involves Privilege Escalation via a Race Condition. This vulnerability is the result of multiple bad practices, making it possible for a user with local network access to compromise the system and escalate their privileges. The file at the center of this vulnerability is: remote.rs
At the time of execution, there is no validation of the script's integrity, and its location in a folder with write permissions for anyone makes it susceptible to potential overwrites, primarily due to a race condition.
Exploitation
To exploit this vulnerability, you must first have compromised the server, either remotely or locally, let's call this "User 1". Then, another user, either local or remote, with higher privileges, such as the "root" user, attempts to connect to the server using Lapce. At this point, the script that User 1 is overwriting will be executed by the "root" user when attempting to connect to the server. In summary, you need initial access to the server as User 1 and then wait for User 2, who has higher privileges, to try to connect using Lapce for the script to be executed with those privileges. You must go to the tmp directory and execute the following commands:
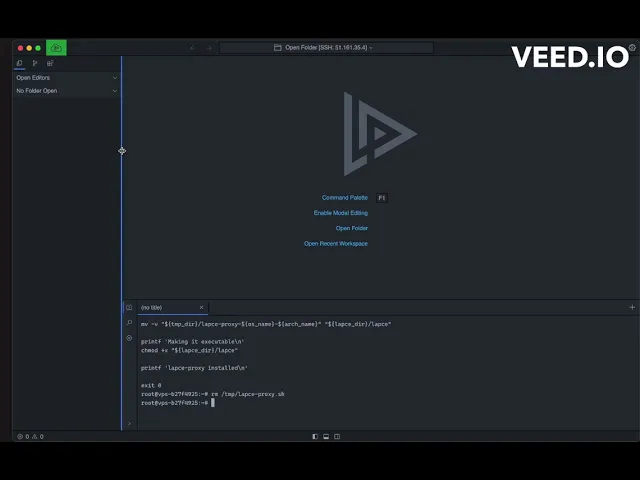
Evidence of exploitation
It's important to note that this vulnerability arises due to the downloading of a file to a directory where any user can write files. If the file is created at the same time it's being downloaded, it can be overwritten, allowing an attacker to manipulate the script's original operation and potentially achieve privilege escalation on the system. To exploit this vulnerability, simply utilize the provided Proof of Concept (PoC) code in the console and wait for a user to attempt to log into a remote server using the SSH service implemented by Lapce. This attack scenario only occurs if the script is created before Lapce generates it; if it's already generated, you would need to wait until the temporary content is deleted. For a more detailed demonstration of the exploitation process, please refer to the following video."
The significant impact of this vulnerability is the potential for a user to escalate privileges by executing commands as that user. The following video demonstrates how this can be achieved:
Our security policy
We have reserved the ID CVE-2023-3891 to refer to this issue from now on. Disclosure policy
System Information
Version: Lapce v0.2.8 (2023-06-01)
Operating System: MacOS
Mitigation
There is a patched code of Lapce available on Github.
References
Vendor page https://lapce.dev/
Patch https://github.com/lapce/lapce/releases/tag/v0.3.0
Credits
The vulnerability was discovered by Renzo Machado from Fluid Attacks' Offensive Team.
Timeline
Aug 8, 2023
Vulnerability discovered
Aug 9, 2023
Vendor contacted
Aug 9, 2023
Vendor replied
Aug 9, 2023
Vendor confirmed
Aug 19, 2023
Vulnerability patched
Sep 18, 2023
Public disclosure
Does your application use this vulnerable software?
During our free trial, our tools assess your application, identify vulnerabilities, and provide recommendations for their remediation.